If you’re looking to build serious muscle and increase strength without counting carbs, the 7-Day Carnivore Diet Meal Plan might be exactly what you need. The carnivore diet — built around nutrient-dense animal foods like steak, eggs, and organ meats — provides complete proteins, healthy fats, and critical muscle-building nutrients like creatine and B vitamins.
Unlike traditional bulking diets that rely on high carbs and processed foods, this meat-based muscle-building plan focuses purely on what your body needs to grow: high-quality protein, recovery-boosting fats, and zero fluff. Whether you’re a seasoned lifter or just getting started with strength training, this full guide will walk you through the benefits, key foods, training tips, and a detailed 7-day meal plan designed to support lean gains and optimal performance.
What Is the Carnivore Diet and How It Supports Muscle Growth
Carnivore Diet Explained
Carnivore Diet Meal Plan:The carnivore diet is a high-protein, animal-based eating plan that eliminates all plant foods — meaning no vegetables, fruits, grains, legumes, nuts, or seeds. Instead, it focuses entirely on meat, fish, eggs, and animal-derived products like butter, tallow, and cheese (if tolerated). It’s essentially the most extreme version of a low-carb diet, often referred to as zero-carb or an all-meat diet.
This dietary approach is rooted in the belief that animal foods provide all the essential nutrients the human body needs to thrive — including complete proteins, essential fatty acids, vitamins A, D, K2, and B12, iron, zinc, and creatine — all of which play a vital role in muscle growth and strength.
Unlike keto or paleo diets that still allow plant-based carbs, the carnivore diet goes a step further by fully cutting out carbs. This shifts the body into a fat-burning state similar to ketosis, but without the fiber or plant-based compounds that some individuals find inflammatory or disruptive to digestion.
For bodybuilders and strength athletes, this diet offers a clean, consistent fuel source and a rich supply of muscle-building amino acids, making it easier to build muscle and recover from heavy training sessions.
Common foods on a carnivore diet include:
- Ribeye steak (fatty and protein-rich)
- Ground beef
- Eggs
- Organ meats (like liver and heart for nutrient density)
- Fatty fish (like salmon and sardines)
- Animal fats (like beef tallow and butter)
By removing plant foods, many people report better digestion, reduced inflammation, improved recovery times, and even higher energy levels during workouts — all of which support better performance and results in the gym.
In short, the carnivore diet is a streamlined, high-protein approach to eating that supports muscle growth, reduces dietary distractions, and fuels serious strength gains.
Muscle-Building Benefits of Animal-Based Nutrition
When it comes to building muscle and gaining strength, animal-based nutrition offers some of the most powerful and bioavailable tools in the dietary arsenal. Unlike plant-based proteins, which are often incomplete or harder to digest, animal foods provide a complete amino acid profile, which is essential for muscle protein synthesis — the process your body uses to repair and grow muscle after training.
Here are some of the top muscle-building advantages of eating a carnivore or animal-based diet:
1. Complete Proteins with High Bioavailability
Animal proteins — found in beef, eggs, poultry, and fish — contain all nine essential amino acids in the exact ratios your body needs for optimal recovery and muscle growth. These proteins are also more easily absorbed and utilized by the body compared to plant-based sources like beans or soy.
Key amino acids like leucine, valine, and isoleucine (known as branched-chain amino acids or BCAAs) are abundant in red meat and play a critical role in triggering muscle protein synthesis. This makes animal-based diets incredibly efficient for fueling hypertrophy and recovery.
2. Naturally Rich in Muscle-Supporting Nutrients
Animal foods aren’t just about protein — they come packed with muscle-enhancing micronutrients, many of which are difficult or impossible to get in sufficient amounts from plant foods:
- Creatine – Naturally found in red meat, it improves strength, power, and muscular endurance.
- Vitamin B12 – Supports energy metabolism and red blood cell production for oxygen delivery during workouts.
- Iron (heme) – The most bioavailable form of iron, crucial for strength, oxygen transport, and performance.
- Zinc and Magnesium – Support testosterone levels, recovery, and protein metabolism.
- Collagen and Glycine – Found in connective tissue and bone broth, helpful for joint health and injury prevention.
3. Hormonal and Metabolic Optimization
An animal-based diet rich in saturated fats and cholesterol supports the natural production of key anabolic hormones like testosterone, which plays a critical role in muscle growth, strength development, and motivation in the gym. Contrary to outdated myths, dietary cholesterol from eggs, steak, and liver does not raise heart disease risk in healthy individuals — but it does contribute to hormone synthesis and improved muscle recovery.
Additionally, by eliminating carbs and sugars, carnivore diets help regulate insulin levels and reduce inflammation, creating a more anabolic internal environment and supporting lean mass retention even while cutting fat.
In summary, animal-based nutrition provides the complete toolkit for muscle building — from high-quality protein and recovery-supporting fats to a wide range of strength-enhancing vitamins and minerals. Whether you’re bulking or maintaining lean mass, the carnivore approach delivers clean fuel and targeted nutrients to support your gains from every angle.
Carnivore Diet vs. Other Muscle Gain Diets
Carnivore Diet Meal Plan:When it comes to gaining muscle and increasing strength, there’s no shortage of dietary strategies — from traditional high-carb bulking diets to popular low-carb plans like keto or paleo. So how does the carnivore diet compare to these more common muscle-building approaches?
Let’s break it down by looking at key differences in macronutrients, digestion, inflammation, and sustainability — all of which play a major role in performance and results.
1. Carnivore vs. High-Carb Bulking Diets
Traditional bulking diets typically rely on high amounts of carbohydrates — often from rice, pasta, oats, and even junk food — to increase calories and fuel workouts. While carbs can help with glycogen storage and short-term performance, they can also lead to:
- Fat gain alongside muscle gain
- Energy crashes from insulin spikes
- Digestive issues from excess fiber or processed carbs
In contrast, the carnivore diet emphasizes clean, calorie-dense animal foods that provide consistent energy without blood sugar swings. With high protein and fat intake, your body relies on fat as a stable energy source while still getting the amino acids it needs for recovery and muscle growth.
Bonus: On carnivore, many lifters report leaner gains with less bloating and fat accumulation.
2. Carnivore vs. Keto Diet
While both diets are low-carb, there’s a critical distinction: keto still includes plant-based foods, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, avocados, and fiber-rich vegetables. For some people, these can cause:
- Digestive discomfort (bloating, gas)
- Hidden anti-nutrients (like oxalates and lectins)
- Difficulty hitting high protein targets for muscle gain
The carnivore diet simplifies things by removing all plant-based variables, focusing solely on animal products that are nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory, and rich in creatine, carnitine, and collagen — all of which enhance training, recovery, and muscle growth.
Additionally, keto often prioritizes fat over protein, which may not be ideal for those focused on hypertrophy. Carnivore, on the other hand, naturally delivers higher protein intake when built around meat-heavy meals.
3. Carnivore vs. Paleo and “Clean Eating”
Paleo diets emphasize whole foods, including lean meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds. While cleaner than the standard diet, it still includes a lot of fibrous and plant-based carbohydrates that may not suit everyone, especially those with autoimmune issues or gut sensitivity.
The carnivore diet strips things down to the essentials, which means:
- Easier digestion and nutrient absorption
- Reduced food volume with higher calorie density
- Elimination of potential allergens or irritants from plant foods
This makes carnivore more sustainable for some lifters, especially those who thrive on routine and want to avoid the complexity of macro counting, meal prepping, or dealing with food sensitivities.
Bottom Line: While every diet has its pros and cons, the carnivore diet stands out for its simplicity, nutrient density, and consistent support for strength and muscle growth. It removes guesswork, minimizes bloating, and ensures your body is fueled with nothing but the most anabolic foods nature provides.
For many, it’s not just a diet — it’s a performance-focused lifestyle.
Key Foods for a High-Protein Carnivore Diet
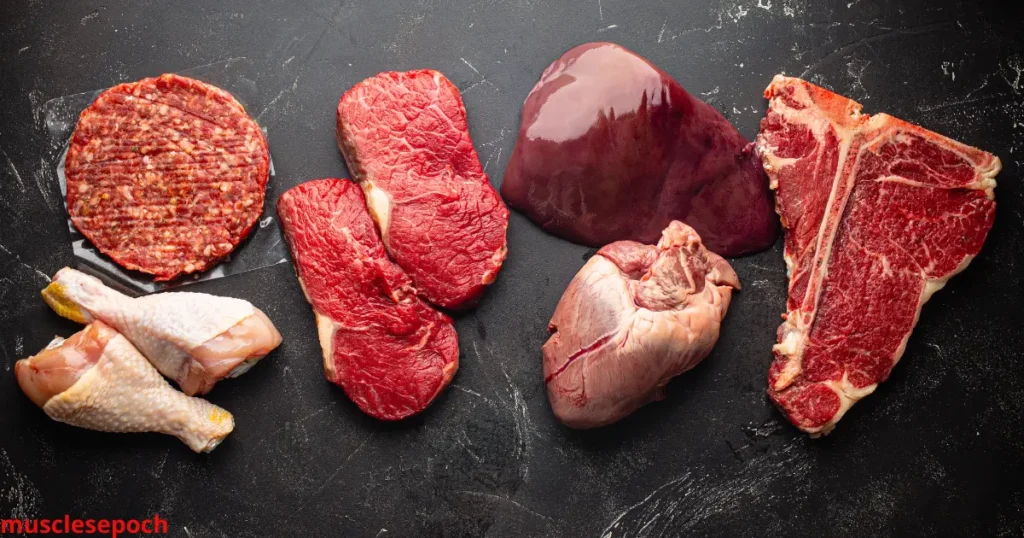
Muscle-Building Meats to Include
When you’re following a 7-day carnivore diet meal plan for building muscle and strength, not all meats are created equal. While all animal products offer complete proteins and essential nutrients, certain cuts of meat are especially effective at supporting muscle growth, strength, and recovery.
Below are the top muscle-building meats to include in your plan — chosen for their amino acid content, fat-to-protein ratio, nutrient density, and anabolic potential.
1. Ribeye Steak
Ribeye is the gold standard for muscle-building on the carnivore diet. It’s rich in high-quality protein and naturally marbled with fat — making it ideal for maintaining hormonal balance, boosting satiety, and fueling intense strength workouts.
- High in creatine, iron, zinc, and B vitamins
- Ideal 1:1 fat-to-protein ratio supports bulking and recovery
- Contains collagen and connective tissue to support joint health
Pro Tip: Aim for grass-fed ribeye when possible for better omega-3 and CLA content.
2. Ground Beef (80/20 or 70/30)
Ground beef is not only cost-effective but extremely versatile. Opt for 80/20 or 70/30 blends, which provide enough fat to support energy needs and testosterone production while delivering all the essential amino acids required for hypertrophy.
- Easy to prep in bulk for meal plans
- Can be used in burgers, bowls, or as a base for carnivore casseroles
- Rich in iron and carnosine — critical for muscle function and endurance
This is a staple in many muscle-building carnivore meal plans, especially for those eating multiple meals per day.
3. Organ Meats (Liver, Heart, Kidney)
While not traditionally favored by bodybuilders, organ meats are nutrient powerhouses that support everything from recovery and immunity to testosterone production and energy metabolism.
- Beef liver: Nature’s multivitamin — rich in vitamin A, B12, iron, and folate
- Beef heart: High in CoQ10, taurine, and zinc — all beneficial for endurance and cardiovascular support
- Kidney: Great source of selenium and helps support the body’s detox pathways
Including a few ounces of organ meats per week can significantly enhance micronutrient intake, which is often overlooked in conventional bulking diets.
Bonus Picks for Muscle Growth:
- Eggs: Complete protein, choline, healthy cholesterol for hormone support
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines): Rich in omega-3s for inflammation control and joint health
- Lamb and bison: Great alternatives to beef with unique nutrient profiles
Bottom Line: For maximum muscle growth on a carnivore diet, prioritize fatty, nutrient-dense cuts of meat that support both anabolism and recovery. By rotating between ribeye, ground beef, and organ meats — and supplementing with eggs or fish if desired — you’ll ensure your body is getting the full spectrum of nutrients it needs to train hard and grow stronger.
Optimal Protein and Fat Ratios for Strength
One of the most important — yet often overlooked — aspects of success on a carnivore diet for muscle and strength is getting the right balance between protein and fat. While high-protein intake is essential for muscle growth, dietary fat plays a critical role in fueling workouts, supporting hormone production, and optimizing recovery.
On a carb-free or low-carb plan like carnivore, fat becomes your primary energy source — not carbs. That’s why eating lean meat alone isn’t enough. You need the right protein-to-fat ratio to support both muscle repair and the metabolic demands of strength training.
1. Why Fat Is Essential on Carnivore
Many athletes are conditioned to think of fat as the enemy, but on the carnivore diet, fat is fuel. Without carbs to provide energy, your body shifts into fat-burning mode (ketosis), relying on dietary fat and stored fat to power your workouts and daily function.
Fat also plays key roles in:
- Testosterone production — especially from saturated and cholesterol-rich sources like egg yolks and red meat
- Joint lubrication and recovery
- Cognitive focus and energy stability during long training sessions
- Absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K2)
If you don’t consume enough fat, especially on a zero-carb diet, you may feel:
- Fatigued or mentally foggy
- Sore and slow to recover
- Stalled in muscle growth due to hormone imbalance
2. Recommended Protein-to-Fat Ratios for Strength Gains
There’s no one-size-fits-all ratio, but here are common guidelines for building muscle on carnivore:
- 70% fat / 30% protein (by calories) – Best for beginners transitioning into carnivore, promotes energy, supports hormone levels, and minimizes cravings.
- 60% fat / 40% protein – Ideal for lifters who want to maximize protein synthesis while maintaining enough fat for fuel.
- 50/50 ratio – A more aggressive, lean-gain approach, better suited for those in a caloric surplus or who have adapted to fat metabolism and need more protein for recovery.
Note: These percentages are based on calories, not grams. Since fat contains 9 calories per gram and protein only 4, even small amounts of fat add up quickly.
3. How to Adjust Your Ratios Based on Training Goals
Your ideal protein-to-fat ratio depends on your goals, metabolism, and training style:
- For strength and size (bulking):
Prioritize higher fat intake (65–70%) to ensure hormonal support and caloric surplus. - For lean muscle preservation (cutting):
Go slightly higher in protein (50–60%) to retain muscle mass while reducing total calories. - For performance and recovery:
Aim for a balanced 60/40 split, ensuring adequate fat for energy and enough protein for repair.
You can tweak your ratio by:
- Choosing fattier cuts (ribeye, ground beef 70/30, pork belly)
- Adding animal fats (butter, tallow, suet)
- Including eggs and organ meats with healthy fats
Bottom Line: For strength training on a carnivore diet, balancing protein and fat is crucial. Too much lean meat can leave you fatigued, while too little protein can slow down gains. The sweet spot lies in fueling with fat and repairing with protein, dialing in your ratio based on your goals. Start with a 60–70% fat / 30–40% protein range, and adjust as needed for your body and training intensity.
Supplements to Consider on a Carnivore Diet

One of the core benefits of the carnivore diet is its simplicity — you’re getting most of your nutrients from whole, nutrient-dense animal foods. However, even with a well-structured carnivore meal plan, there may be certain gaps or performance-enhancing opportunities where strategic supplementation can make a real difference, especially for those training hard or seeking optimal muscle-building results.
Here’s a breakdown of the most useful carnivore-friendly supplements to consider, categorized by purpose:
1. Muscle Growth & Performance
- Creatine Monohydrate
Even though red meat naturally contains creatine, supplementing with 3–5g daily can help saturate your muscles for increased strength, power output, and endurance — especially important if you’re doing resistance training or high-intensity workouts.
Supports ATP regeneration, improves performance, and boosts lean mass. - Whey Protein (Isolate or Hydrolyzed)
If you’re struggling to hit your daily protein goals or need a quick post-workout option, a high-quality whey isolate (ideally grass-fed) can help. It’s fast-digesting, complete in BCAAs, and compatible with most carnivore approaches.
Great for post-training recovery and meeting daily protein intake. - Electrolytes (Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium)
Carnivore diets are naturally diuretic, meaning you may lose more water and essential minerals through urine. Low electrolytes can lead to fatigue, cramping, and weakness — especially during heavy training cycles.
Use a balanced electrolyte supplement or DIY mix with sea salt, potassium chloride, and magnesium glycinate.
2. Health & Recovery Support
- Vitamin D3 + K2
If you don’t get regular sun exposure, supplementing with vitamin D3 (2,000–5,000 IU) and K2 (MK-7) can support bone density, immune function, and testosterone levels.
Crucial for muscle function, strength, and hormonal balance. - Magnesium Glycinate or Citrate
Helpful for muscle recovery, deep sleep, and preventing cramps. Even with red meat, magnesium levels may be suboptimal — especially in active individuals.
Take before bed for better sleep and nervous system recovery. - Collagen or Gelatin Powder (Optional)
If you’re not eating skin, tendons, or drinking bone broth regularly, a collagen supplement can support connective tissue health, reduce joint pain, and promote faster recovery.
Great for joint integrity and soft tissue resilience during heavy lifting.
3. Gut & Nutrient Absorption (Optional)
- Digestive Enzymes or Betaine HCl
Some people transitioning to carnivore may experience sluggish digestion, especially with high-fat meals. Enzymes can ease the transition and improve protein breakdown.
Useful during the first 2–4 weeks or if eating very large meat portions. - Liver Supplements (Desiccated or Freeze-Dried)
If you’re not a fan of eating liver regularly but want the nutrient density it offers, a freeze-dried organ supplement can fill the gap. Look for grass-fed, hormone-free options.
Boosts vitamin A, B12, iron, and co-factors for muscle metabolism.
Bottom Line: While the carnivore diet is nutrient-dense, targeted supplements can help you maximize performance, muscle gains, and recovery — especially if you train hard, sweat often, or have specific goals like strength or hypertrophy. Focus on essentials like creatine, electrolytes, and magnesium, and consider liver, collagen, or protein powder based on your dietary preferences and training intensity.
Supplement wisely — don’t overcomplicate, and prioritize food first, but use smart additions to fill gaps and support your muscle-building success.
7-Day Carnivore Meal Plan for Muscle and Strength
Daily Meal Structure and Timing
When it comes to building muscle on a carnivore diet, what you eat is just as important as when you eat it. Proper meal timing and structure can significantly impact your performance, recovery, energy levels, and muscle growth.
While the carnivore diet is flexible, athletes and lifters benefit most from an eating strategy that matches their training intensity and recovery demands. Below is a breakdown of how to structure your meals for maximum anabolic effect while staying true to the simplicity of carnivore nutrition.
1. Number of Meals Per Day
There’s no one-size-fits-all, but here are three common meal frequency options:
- 3 Meals Per Day (Optimal for Muscle Gain)
Ideal for those aiming to increase total calorie and protein intake. Spreading meals out ensures constant nutrient delivery and gives your body multiple opportunities for muscle protein synthesis throughout the day.
Example: Breakfast, post-workout lunch, and dinner. - 2 Meals Per Day (Time-Efficient & Still Effective)
Suitable for lifters who prefer fewer meals but larger portions. Works well with an early training session followed by a large post-workout feast, then dinner.
Popular with intermittent fasting-style carnivore approaches. - 1 Meal Per Day (OMAD – Not Ideal for Muscle Building)
While great for fat loss or simplicity, OMAD often doesn’t provide enough total calories or protein for hypertrophy. It’s generally not recommended for serious muscle growth goals.
2. Meal Timing Around Training
Pre-Workout Meal (Optional, 1–2 Hours Before Training):
If you’re training early in the day or doing strength work, a light-to-moderate meal of protein and fat can help fuel performance.
- Example: 2–3 eggs, 3 oz of steak or bacon
Post-Workout Meal (Essential):
This is the most important meal of the day for lifters. Aim for a large portion of fatty red meat, which provides amino acids (like leucine and creatine) and the fat your body needs for energy and hormone balance.
- Example: 8–12 oz ribeye steak, 2 eggs, bone broth or collagen-rich stew
Evening Meal (Recovery and Hormone Support):
Focus on nutrient-dense, slower-digesting foods to support overnight muscle repair and sleep quality.
- Example: Ground beef bowl with liver or heart, marrow bones, optional raw cheese
3. Key Timing Considerations for Strength and Hypertrophy
- Spread protein throughout the day: Aim for at least 30–50g of protein per meal to trigger muscle protein synthesis multiple times per day.
- Don’t train fasted (if performance suffers): While some can lift fasted, many lifters feel stronger with a small pre-workout meal.
- Hydrate and replenish electrolytes: Especially around training sessions — sodium, potassium, and magnesium are critical.
- Use bone broth or collagen at night: Supports sleep, joints, and connective tissue recovery.
Tip: If you’re eating only 2 meals, make sure both meals are calorie-dense and include at least 1g of protein per pound of body weight daily for muscle growth.
Bottom Line: For strength and muscle-building on a carnivore diet, meal timing and structure matter. Whether you eat two or three meals a day, be sure to center them around your training schedule, prioritize your post-workout nutrition, and make each meal nutrient-dense with quality animal-based foods. A consistent rhythm of eating, resting, and lifting is key to seeing long-term gains.
7-Day Sample Meal Plan Breakdown
A well-structured 7-day carnivore diet meal plan is your roadmap to consistent muscle growth and strength gains. This plan balances high-quality animal proteins with adequate fats, ensuring you meet your energy needs while promoting recovery and hypertrophy.
Below, we break down what a typical week looks like on the carnivore diet, focusing on variety, nutrient density, and ease of preparation.
Day 1: Kickstart with Classic Beef Cuts
- Breakfast: 3 large eggs cooked in butter, 4 oz beef liver
- Lunch: 10 oz ribeye steak, bone broth
- Dinner: Ground beef (80/20) burger patties with a side of pork belly
Focus: High protein and fat to jumpstart muscle protein synthesis, plus liver for micronutrients.
Day 2: Introducing Organ Meats and Fatty Cuts
- Breakfast: Beef heart sautéed with eggs
- Lunch: 12 oz New York strip steak
- Dinner: Slow-cooked beef chuck roast with marrow bones
Focus: Support connective tissue and joint health with collagen-rich cuts.
Day 3: Incorporating Fatty Fish
- Breakfast: 4 eggs and 3 oz smoked salmon
- Lunch: Ribeye steak (8 oz)
- Dinner: Ground lamb with added tallow
Focus: Omega-3s for inflammation control and muscle recovery.
Day 4: Variety with Poultry and Red Meat
- Breakfast: 3 eggs and bacon
- Lunch: Roasted chicken thighs (skin-on)
- Dinner: Beef brisket slow-cooked
Focus: Balancing muscle-building amino acids with varied fat sources.
Day 5: Organ Meat Boost
- Breakfast: Liver pâté on carnivore-friendly crackers (optional) or plain
- Lunch: Grilled beef heart
- Dinner: Ribeye steak with bone marrow
Focus: Replenishing vitamins and minerals critical for energy metabolism.
Day 6: Leaner Cuts for Recovery
- Breakfast: 4 egg omelet with cheese (optional)
- Lunch: Sirloin steak (lean cut)
- Dinner: Roasted pork belly
Focus: Slightly lower fat intake to support digestion and recovery.
Day 7: Feast Day for Strength Gains
- Breakfast: 4 eggs with sausage (pork or beef)
- Lunch: T-bone steak (12 oz)
- Dinner: Beef short ribs slow-cooked with marrow
Focus: Maximizing calories and protein for muscle growth and strength.
Tips for Success on the 7-Day Plan:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water and bone broth daily.
- Electrolytes matter: Supplement with salt, magnesium, and potassium as needed.
- Listen to your body: Adjust portion sizes based on hunger, training intensity, and recovery.
- Prep in advance: Cook large batches of ground meat or slow-cooked roasts to save time.
- Include variety: Rotate between different meats and organ cuts to cover all micronutrient bases.
Final Thoughts:
Following this 7-day carnivore diet meal plan provides a solid foundation to fuel your workouts, optimize muscle recovery, and build strength without the complexity of counting carbs or calories obsessively. Remember, consistency and quality of food matter most — the simplicity of carnivore makes it easier to stay on track and see results.
Grocery List for the Week
To successfully follow your 7-Day Carnivore Diet Meal Plan for Building Muscle and Strength, having the right ingredients on hand is essential. This grocery list covers all the necessary animal-based foods, fats, and essential supplements you’ll need to fuel your body, recover well, and maximize muscle gains.
Here’s a comprehensive shopping guide organized by category to make your grocery run efficient and ensure you don’t miss any key nutrient sources.
1. Beef & Red Meat
- Ribeye steak – 3–4 steaks (8–12 oz each)
- Ground beef (80/20 or 70/30) – 3–4 lbs
- New York strip steak – 2 steaks (8–10 oz each)
- Beef chuck roast – 2–3 lbs
- Beef brisket – 2 lbs
- Beef heart (organ meat) – 1–2 lbs
- Beef liver (organ meat) – 1 lb
- Beef short ribs – 2 lbs
- Bone marrow bones – 2–3 lbs (for broths or roasting)
2. Poultry & Other Meats
- Chicken thighs (skin-on) – 4–6 pieces
- Bacon (preferably nitrate-free) – 1 lb
- Sausage (pork or beef, no fillers) – 1 lb
- Eggs – 2 dozen (large or extra-large)
3. Fat Sources
- Butter or ghee – 1 lb
- Beef tallow or suet – 1 jar or block
- Pork fat (lard) – optional for cooking
- Animal-based cooking fats – as needed
4. Seafood (Optional but Recommended)
- Smoked salmon or fresh fatty fish (salmon, sardines) – 8 oz
- Canned sardines (in water or olive oil) – 2 cans
5. Supplements & Extras
- Bone broth (store-bought or homemade) – 1 quart
- Electrolyte supplement (sodium, potassium, magnesium) – as needed
- Creatine monohydrate – 1 container
- Vitamin D3 + K2 supplement – if needed
- Magnesium supplement – if needed
- Collagen powder (optional) – 1 container
Shopping Tips:
- Choose grass-fed, pasture-raised beef and poultry when possible for higher omega-3s and better nutrient profiles.
- Buy organ meats fresh or frozen — they are nutrient-dense and vital for micronutrient balance.
- Stock up on bone marrow and marrow bones — perfect for nutrient-rich broths that aid recovery.
- Eggs are a powerhouse — inexpensive and packed with protein, fats, and vitamins.
- Check ingredient labels carefully when buying sausages or processed meats to avoid additives or fillers.
- Consider bulk buying or local butcher options to save money and get fresher cuts.
Final Thought:
By keeping this grocery list handy, you’ll simplify meal prep and make sticking to your carnivore diet easy and enjoyable. With a focus on high-quality, fatty cuts of meat, organ meats, and supportive supplements, you’re setting yourself up for optimal muscle growth and strength gains over the week.
Training Tips to Maximize Muscle on Carnivore

Strength Training While on a Carnivore Diet
Combining the carnivore diet with a structured strength training program is a powerful strategy to maximize muscle growth, enhance strength, and optimize body composition. The carnivore diet’s emphasis on high-quality animal proteins and fats provides the essential building blocks your muscles need to repair and grow, while minimizing inflammation and promoting hormonal balance.
Here’s how to effectively approach strength training while following a carnivore lifestyle:
1. Adjusting to Training Without Carbs
The carnivore diet is virtually zero-carb, which means your body will primarily use fat and ketones for energy instead of glucose. This metabolic shift requires some adaptation, especially if you’re accustomed to carb-fueled workouts.
- Adaptation period: Expect the first 1–3 weeks to involve some adjustment — temporary drops in performance or energy are common as your body becomes fat-adapted.
- Maintain training intensity: Once adapted, many lifters report stable or even improved endurance and recovery, thanks to the anti-inflammatory effects of the diet and steady energy from fats.
- Monitor energy levels: Pay attention to signs of low energy or fatigue, and adjust meal timing or fat intake accordingly.
2. Training Frequency and Volume
- Focus on compound lifts: Prioritize multi-joint exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows. These movements recruit large muscle groups, stimulating maximum muscle protein synthesis and strength gains.
- Frequency: Aim for 3-5 training sessions per week, balancing intensity and volume to avoid overtraining.
- Recovery: Carnivore’s nutrient-dense foods support faster recovery, but listen to your body. If soreness or fatigue lingers, incorporate extra rest or light activity days.
3. Post-Workout Nutrition for Muscle Repair
- High-protein, high-fat meals post-workout: Consuming a large portion of fatty animal protein within 1–2 hours after training provides amino acids necessary for muscle repair and fat to replenish energy stores and support hormone production.
- Bone broth or collagen: Including collagen-rich foods or supplements post-workout may improve joint recovery and connective tissue health.
- Hydration and electrolytes: Replenish sodium, potassium, and magnesium lost through sweat to prevent cramping and maintain performance.
4. Managing Hormonal Health
Strength training combined with a carnivore diet can optimize levels of testosterone, growth hormone, and IGF-1 — all key players in muscle growth and strength.
- Diet’s role: Fat intake, particularly saturated fats and cholesterol from animal sources, supports hormone synthesis.
- Sleep and recovery: Prioritize quality sleep, as hormones peak during rest periods. Carnivore diet’s simplicity and potential anti-inflammatory effects may improve sleep quality.
5. Supplements to Support Training
While whole foods form the foundation, consider these supplements to enhance training on carnivore:
- Creatine monohydrate: Boosts strength, power, and recovery.
- Electrolytes: Prevents fatigue and cramping.
- Magnesium: Supports muscle relaxation and sleep quality.
- Collagen: Aids joint and connective tissue health.
Final Thoughts:
Strength training while following a carnivore diet is highly effective for building muscle and boosting strength, provided you give your body time to adapt and support it with nutrient-dense animal foods. Focus on heavy compound movements, prioritize post-workout nutrition, and stay attentive to recovery and hydration. With consistency, the carnivore diet can complement your training to deliver impressive muscle gains and enhanced physical performance.
Recovery and Performance Optimization
Optimizing recovery is just as important as your workouts when it comes to building muscle and strength — especially on a carnivore diet. Proper recovery ensures your muscles repair efficiently, your nervous system rejuvenates, and you can maintain high performance in every training session. The carnivore diet, rich in animal-based nutrients, naturally supports recovery, but pairing it with targeted strategies can take your gains to the next level.
1. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Sleep is when your body produces the majority of its muscle-repairing hormones, including growth hormone and testosterone. Adequate rest enhances protein synthesis and reduces inflammation, helping you recover faster and train harder.
- Tips for better sleep on carnivore:
- Eat a satisfying, protein-rich dinner with some fat to promote satiety and hormone balance.
- Avoid caffeine late in the day, as it can disrupt sleep cycles.
- Consider magnesium supplementation (magnesium glycinate) to support relaxation and improve sleep quality.
2. Leverage Nutrient-Dense Foods for Recovery
The carnivore diet’s abundance of high-quality proteins and healthy fats provides essential amino acids and fat-soluble vitamins critical for muscle repair and inflammation control.
- Protein: Amino acids from meats and organs fuel muscle protein synthesis, the key process for muscle growth.
- Collagen and gelatin: Found in connective tissues and bone broth, these support joint health and tissue repair, reducing injury risk and soreness.
- Micronutrients: Organ meats like liver are packed with vitamin A, B vitamins, zinc, and iron, all vital for recovery and energy metabolism.
3. Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances can lead to muscle cramps, fatigue, and poor performance.
- Carnivore diuresis: The low-carb nature of the diet causes increased water loss, making it crucial to replenish fluids and electrolytes.
- Electrolyte tips: Supplement sodium (via salt), potassium, and magnesium, especially around workouts, to maintain optimal muscle function and avoid cramps.
4. Active Recovery and Mobility Work
Incorporating active recovery days, including light cardio, stretching, or mobility drills, promotes blood flow to muscles, enhancing nutrient delivery and waste removal.
- Why it matters: Improved circulation speeds up healing, reduces stiffness, and prepares muscles for the next heavy session.
- Recommended practices: Gentle walking, foam rolling, dynamic stretching, or yoga-style movements.
5. Supplement Support for Recovery
While the carnivore diet covers many bases, some supplements can enhance recovery and performance:
- Creatine: Beyond strength gains, creatine helps reduce muscle damage and inflammation post-exercise.
- Magnesium: Supports muscle relaxation and nervous system health.
- Collagen peptides: Helps rebuild connective tissues and joints.
- Omega-3s (from fatty fish or supplements): Reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health.
Final Takeaway:
Optimizing recovery on a carnivore diet involves more than just what you eat — it’s about quality sleep, hydration, active recovery, and strategic supplementation. By integrating these elements with your nutrient-rich carnivore meals, you’ll enhance muscle repair, reduce injury risk, and sustain high performance for every workout, setting the stage for consistent muscle growth and strength gains.
Tracking Progress and Adjustments
Successfully building muscle and strength on a 7-Day Carnivore Diet Meal Plan requires more than just following the meals and workouts—it also demands consistent tracking and smart adjustments. Monitoring your progress helps you identify what’s working, pinpoint challenges, and tailor your approach for optimal results.
Here’s how to effectively track your progress and make necessary tweaks while following the carnivore diet and strength training regimen.
1. Key Metrics to Monitor
- Body Weight and Composition:
Use a reliable scale to track your weight weekly. To get a fuller picture, consider using body composition tools like skinfold calipers, bioelectrical impedance scales, or even professional DEXA scans to measure muscle gain versus fat loss. - Strength Improvements:
Keep a detailed workout log recording your lifts, sets, reps, and weights. Increases in strength on compound movements (squat, deadlift, bench press) are strong indicators of muscle growth and training effectiveness. - Visual Progress:
Take progress photos weekly or bi-weekly from multiple angles. Muscle growth, improved definition, and fullness often show before the scale moves significantly. - Energy and Recovery:
Note your daily energy levels, training performance, and recovery times. Feeling fatigued or stalled could indicate a need for dietary or training adjustments.
2. Adjusting Your Diet
- Caloric Intake:
If you’re not gaining muscle or strength after a few weeks, gradually increase your calorie intake by adding more fatty cuts of meat or extra eggs. The carnivore diet is naturally satiating, so mindful increases are key. - Protein Targets:
Aim for at least 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight daily. If gains plateau, slightly boost protein or meal frequency. - Fat Ratios:
Adjust fat intake to support energy needs. If you experience low energy, add more fatty cuts like ribeye or pork belly. Conversely, reduce fat slightly if you notice unwanted fat gain. - Hydration & Electrolytes:
Monitor signs of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance (muscle cramps, fatigue) and adjust water and salt intake accordingly.
3. Fine-Tuning Training
- Volume and Intensity:
If progress stalls, increase the weight lifted, add sets, or adjust training frequency. Progressive overload is essential for continuous muscle growth. - Deload Weeks:
Incorporate lighter training weeks every 4–6 weeks to allow full recovery and prevent burnout. - Exercise Variation:
Rotate exercises to target muscles from different angles and prevent plateaus.
4. Listen to Your Body
- Track Mood and Well-being:
Changes in mood, sleep quality, or digestion can be subtle signals that your current diet or training needs modification. - Rest Days:
Ensure you’re incorporating sufficient rest days to promote recovery. - Fatigue and Performance:
Prolonged fatigue or decline in workout performance might mean you need more calories, better sleep, or more recovery time.
5. Use Technology and Tools
- Apps:
Use apps like MyFitnessPal (customized for carnivore macros), Strong, or Fitbod to log nutrition and workouts easily. - Wearables:
Devices tracking sleep quality, heart rate variability, and daily activity can offer valuable insights into your recovery status.
Final Thoughts:
Tracking your progress while following a carnivore diet for muscle and strength allows you to make informed, data-driven adjustments that accelerate your results. Regularly assessing your body composition, strength gains, energy levels, and recovery ensures you stay on course. Remember, flexibility is key—use your tracked data to tweak your diet and training plan, helping you overcome plateaus and continue building muscle efficiently.
Conclusion
The carnivore diet may seem unconventional, but for many lifters, it offers a powerful and sustainable way to build muscle, boost strength, and simplify nutrition. With its focus on high-protein, nutrient-dense animal foods, this 7-day meal plan provides all the building blocks your body needs — without the inflammation, bloat, or complexity of standard bodybuilding diets.
By combining this plan with a solid strength training routine and proper recovery, you’ll be well on your way to lean gains and better performance. Stick with it, track your results, and adjust as needed — and you might just find that the carnivore diet is your secret weapon for serious muscle and strength.

